Authentication Methods
Integration authentication methods have advantages over existing ebs SSO (single sign-on) mechanisms, for example:
-
Access is not restricted to the ebs host location
-
Available to users that are not signed into a device on your network
-
Compatible with Multi Factor Authentication (MFA) methods
Select from the following to view supported modules:
The ebs modules that support Microsoft Entra ID from ebs 4.32 are:
-
ebs: ontrack Hub
-
ebs: ontrack Learner Hub
-
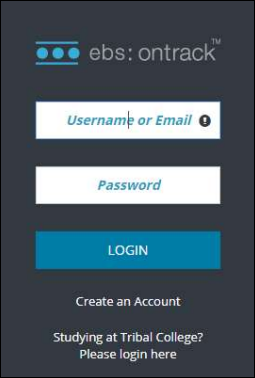
The Login button supports access with ebs credentials.
Clicking the Studying at tribal college? Please login here button allows authentication with Microsoft Entra ID credentials.
Alternatively, you can use your organisation's authentication page.
-
ebs: intel
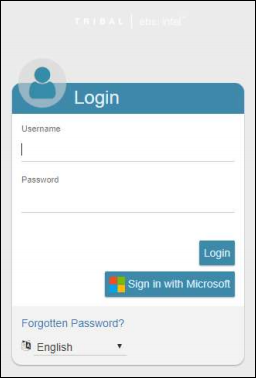
The Login button supports access with intel credentials.
Clicking the Sign in with Microsoft button allows authentication with Microsoft Entra ID credentials.
The ebs modules that support Microsoft Entra ID from ebs 4.37 are:
-
ebs: central
-
ebs: shape
You can use dual authentication to allow your users to log in with either their ebs credentials or their Microsoft Entra ID credentials.
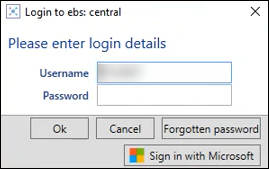
You can enable dual authentication to display the Login to ebs: central window.
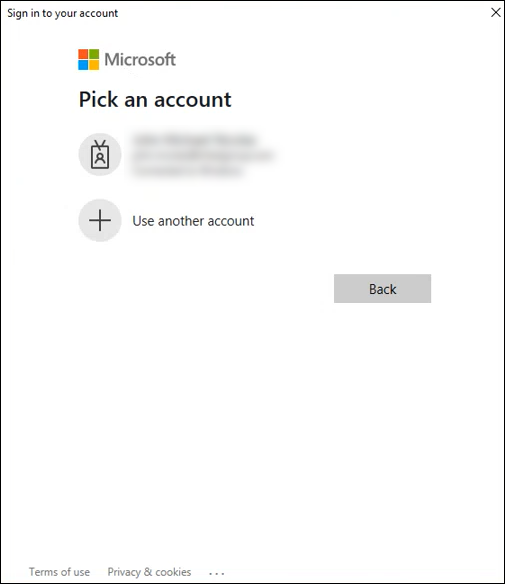
Alternatively, you can disable dual authentication to bypass the ebs login stage and display the Sign in to your account window.
Note: Refer to ebs Client Authentication for Microsoft Entra ID for further information
The ebs modules that support Google Workspace from ebs 4.33 are:
-
ebs: ontrack Hub
-
ebs: ontrack Learner Hub
-
ebs: ontrack Teaching and Learning
The Login button supports access with ebs credentials.
Clicking the Studying at tribal college? Please login here button allows authentication with Google Workspace credentials.
Alternatively, you can use your organisation's authentication page.

Note: When authenticating with Microsoft Entra ID or Google Workspace, users are transferred to their organisation's Microsoft 365 or Google login page, where they may be either automatically authenticated or required to enter their login credentials, depending on policies and previous authentication actions.